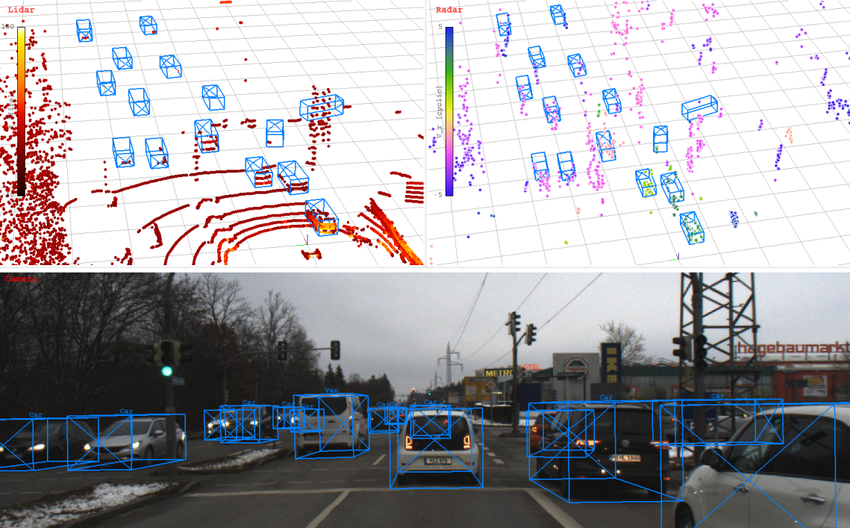
3D Multi – Lane Radar
In the vast system of intelligent transportation systems, precise perception capabilities undoubtedly represent the core factor determining their success or failure. The 3D multi – lane radar, with its excellent performance and unique technical advantages, is becoming a crucial part of intelligent transportation systems. Like a “super eye”, it provides accurate and comprehensive environmental perception information for the entire system, leading intelligent transportation technology to new heights.
I. Technological Breakthroughs with Millimeter – Level Precision
1. Multi – Beam Matrix Architecture: The Core Support for Precise Angle Measurement
In the field of radar technology, angle measurement accuracy is one of the key indicators to measure its performance. Traditional radars often have large errors in angle measurement and are difficult to meet the strict requirements of modern intelligent transportation systems for high precision. The 3D multi – lane radar, however, achieves an amazing ±0.1° angle measurement accuracy by using an advanced 128 – channel active phased – array antenna, which is a 30 – fold improvement compared to traditional radars.
The 128 – channel active phased – array antenna is the core component of the 3D multi – lane radar’s multi – beam matrix architecture. It consists of numerous tiny antenna elements, each of which can independently transmit and receive electromagnetic wave signals. By precisely controlling the phase and amplitude of the signals emitted by each antenna element, the radar can flexibly adjust the beams in different directions. This precise beam – control technology enables the radar to accurately detect the position of target objects within an extremely narrow angular range.
In practical applications, the advantages of the multi – beam matrix architecture are fully demonstrated. Take the highway scenario as an example. When multiple cars are driving in different lanes, traditional radars may have difficulty accurately distinguishing the specific angles of adjacent vehicles, resulting in deviations in judging vehicle driving trajectories. In contrast, the 3D multi – lane radar, with its ±0.1° high – precision angle – measurement ability, can clearly identify the exact position and driving direction of each vehicle, providing a reliable basis for subsequent traffic management and autonomous driving decisions.
2. Dynamic Compensation Algorithm: The Guardian of Precision in Extreme Environments
In complex and variable traffic environments, external factors such as temperature and vibration can significantly affect the accuracy of radars. Vibration suppression technology is mainly used to address the interference of vehicle vibrations during driving on radar accuracy. Whether on a flat highway or a bumpy rural road, vehicles will inevitably vibrate. This vibration can cause slight displacements of the radar’s antenna, leading to deviations in the transmission and reception of radar signals. The vibration suppression technology of the 3D multi – lane radar uses advanced sensors and algorithms to monitor the radar’s vibration in real – time. Through signal processing and compensation, it eliminates the impact of vibrations. When a 3D multi – lane radar is installed on a vehicle driving on a rugged mountain road, even if the vehicle is severely jolted, the radar can still work stably and accurately detect the surrounding traffic conditions.
3. Super – Resolution Imaging Technology: A Great Leap in Ranging Accuracy
Traditional radars have large errors in ranging, usually only achieving meter – level accuracy, which is far from sufficient in the field of intelligent transportation where high precision is required. The 3D multi – lane radar adopts an advanced compressive sensing algorithm to achieve super – resolution imaging technology, reducing the ranging error of traditional radars from meter – level to ±2mm, representing a huge leap in ranging accuracy.
The compressive sensing algorithm is a new – type signal processing technology based on signal sparsity. In the process of radar signal processing, it can recover high – resolution target images from a small amount of sampled data. Traditional radars need to collect a large amount of data to obtain high resolution, which not only increases the system complexity and cost but also prolongs the data processing time. The compressive sensing algorithm, by taking advantage of the sparse characteristics of target objects in certain transform domains, only needs to collect a small amount of key data to reconstruct the accurate image of the target object.
In practical applications, the super – resolution imaging technology enables the 3D multi – lane radar to measure the distance to target objects with extreme precision. In urban road traffic monitoring, for a queue of vehicles waiting for a traffic light, the 3D multi – lane radar can accurately measure the distance between each vehicle with an error of only ±2mm. This high – precision ranging ability provides strong support for functions such as vehicle distance maintenance and collision warning in intelligent transportation systems.
II. In – Depth Empowerment of Intelligent Transportation Scenarios
1. Intelligent Intersection Solutions
Intelligent intersections are an important part of intelligent transportation systems. They improve the traffic flow efficiency of intersections and reduce the occurrence of traffic accidents through real – time monitoring and optimized control of intersection traffic flow. The 3D multi – lane radar plays a crucial role in intelligent intersection solutions.
2. A New Paradigm for Vehicle – Road Collaboration