Basic understanding of MIMO radar
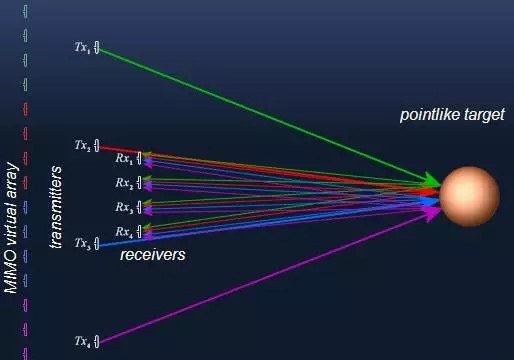
The concept of multiple input multiple output radar was first proposed by Fishie in 2004. It’s not that MIMO technology only started in 2004, but that FIshie first introduced the spatial diversity perspective of MIMO communication into radar.
Based on multi element antennas, MIMO radar uses M channels to transmit mutually orthogonal signals. The multi waveform signals remain independent in space and are received by N receiving elements after being scattered by the target. Each element uses M matched filters to match the echoes, thus obtaining M * N channels of echo data.
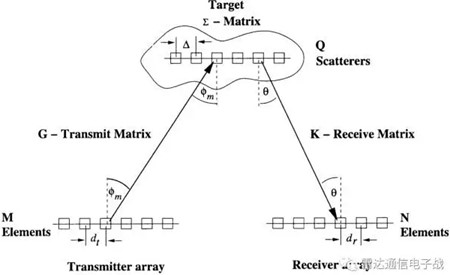
It can be seen that the number of observation channels formed (M * N) can be multiplied by the number of physical elements (M+N), but since the transmitted signal is an orthogonal signal, it cannot be synthesized in spatial power through beamforming like phased array, resulting in a decrease of 1/M in the main lobe gain of the transmitted beam.
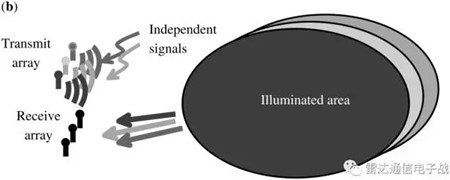
There are two main systems developed based on the different spatial distributions of antenna arrays: statistical MIMO radar and coherent MIMO radar.
Statistical MIMO radar (distributed)
The transmission array is scattered in space, and the target echo is composed of a large number of scattered echoes. The receiver uses orthogonality to separate the echoes at different positions, which are considered statistically independent of each other. The power of the target transmission signal is approximately stable, which is beneficial for target detection and can effectively overcome the radar performance degradation caused by target flicker.
Coherent MIMO radar (compact)
The spatial distribution of the transmitting/receiving array elements is compact, which refers to the correlation between the far-field target echo and the transmitting/receiving antenna array when the spacing between the antenna elements is on the wavelength level of the transmitted signal.
Coherent MIMO radar can be divided into single station and dual station, with single station being easy for everyone to understand; Dual station refers to a compact configuration of receiving and transmitting, which meets the requirements of a dual station radar between them.
For coherent MIMO radar, the positions of each transmitting and receiving unit are known. By phase shifting and adding the MN output signals after matching filtering at the receiving end, beams can be formed in one or more directions.
